10 Best 3D Scanners 2026 in the United States
Winner
Revopoint Trackit Optical Tracking 3D Scanner for 3D Printing, Metrology-Grade Precision 0.02mm, Blue Laser Scans, Marker-Free Scans, Ultra-Realistic Texture Mapping for 3D Modeling
The Revopoint Trackit 3D Scanner stands out for its impressive precision, boasting a resolution and accuracy of up to 0.02mm, which is excellent for professional use in industrial quality control, reverse engineering, and detailed modeling. Its dual scanning modes (30-line cross-laser and single-line laser) offer flexibility to scan both large and small objects effectively. A key strength is its marker-free optical tracking system, allowing you to scan without placing sticky markers on your subject, making the process more convenient and less intrusive.
Most important from
43 reviews
Revopoint MetroY Pro 3D Scanner for 3D Printing, Up to 0.01mm Precision, 34+15+1 Industrial Blue Laser Handheld Scanner, 62-Line Full-Field, Real-time Preview, Bulit-in Wi-Fi 6, Full-Color 3D Scan
The Revopoint MetroY Pro is a handheld 3D scanner designed to deliver very high precision, boasting up to 0.01 mm resolution and 0.02 mm accuracy, which is excellent for detailed projects like 3D printing or reverse engineering. Its advanced blue laser technology and five scanning modes—including a fast 62-line full-field mode—allow it to capture a variety of objects, even shiny or dark surfaces, without needing special sprays. Scanning speed reaches up to 1.7 million points per second, helping you complete jobs quickly.
Most important from
43 reviews
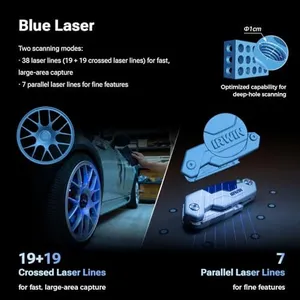
Creality 3D Scanner Raptor Pro for Automotive & Engineering Projects with Metrology-Grade 0.02mm Accuracy,22+7 Blue Laser, Up to 60FPS Scanning Speed
The Creality 3D Scanner Raptor Pro is a solid choice for users needing high precision scanning, especially in automotive and engineering projects. It offers metrology-grade accuracy of up to 0.02mm, thanks to its unique combination of 22 cross laser lines and 7 parallel blue laser lines. This allows it to handle both small intricate parts and larger objects efficiently. Scanning speed is impressive, reaching up to 60 frames per second, which helps reduce the time spent capturing detailed 3D data. The scanner's anti-shaking design and one-shot 3D imaging technology mean it can deliver stable, reliable scans even when used handheld or in less stable environments. Weighing only 405 grams, it’s quite portable and suitable for both workshop and on-site use.
Most important from
15 reviews
Top 10 Best 3D Scanners 2026 in the United States
Winner
Revopoint Trackit Optical Tracking 3D Scanner for 3D Printing, Metrology-Grade Precision 0.02mm, Blue Laser Scans, Marker-Free Scans, Ultra-Realistic Texture Mapping for 3D Modeling
Revopoint Trackit Optical Tracking 3D Scanner for 3D Printing, Metrology-Grade Precision 0.02mm, Blue Laser Scans, Marker-Free Scans, Ultra-Realistic Texture Mapping for 3D Modeling
Chosen by 1169 this week
Revopoint MetroY Pro 3D Scanner for 3D Printing, Up to 0.01mm Precision, 34+15+1 Industrial Blue Laser Handheld Scanner, 62-Line Full-Field, Real-time Preview, Bulit-in Wi-Fi 6, Full-Color 3D Scan
Revopoint MetroY Pro 3D Scanner for 3D Printing, Up to 0.01mm Precision, 34+15+1 Industrial Blue Laser Handheld Scanner, 62-Line Full-Field, Real-time Preview, Bulit-in Wi-Fi 6, Full-Color 3D Scan
Creality 3D Scanner Raptor Pro for Automotive & Engineering Projects with Metrology-Grade 0.02mm Accuracy,22+7 Blue Laser, Up to 60FPS Scanning Speed
Creality 3D Scanner Raptor Pro for Automotive & Engineering Projects with Metrology-Grade 0.02mm Accuracy,22+7 Blue Laser, Up to 60FPS Scanning Speed
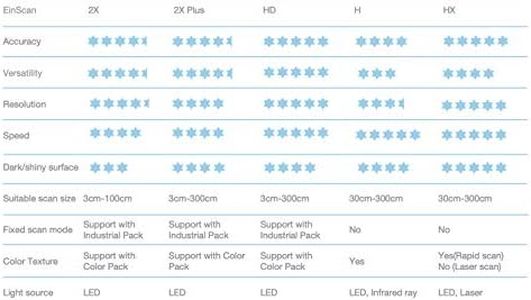
EinScan Pro HD Handheld 3D Scanner with Industrial Pack, Color Pack, Solid Edge Shining3D CAD Software, 0.2mm Resolution, 0.04mm Accuracy for Reverse Engineering, 3D Modeling, Art, Design, Healthcare
EinScan Pro HD Handheld 3D Scanner with Industrial Pack, Color Pack, Solid Edge Shining3D CAD Software, 0.2mm Resolution, 0.04mm Accuracy for Reverse Engineering, 3D Modeling, Art, Design, Healthcare
Shining3D EinScan Rigil 3D Scanner - Wireless & All-in-One Portable Scanner with Scanning Software, 0.04mm Accuracy, 38 Laser Lines for Reverse Engineering, Manufacturing, Art and Design
Shining3D EinScan Rigil 3D Scanner - Wireless & All-in-One Portable Scanner with Scanning Software, 0.04mm Accuracy, 38 Laser Lines for Reverse Engineering, Manufacturing, Art and Design
EINSTAR Rockit Wireless Laser 3D Scanner, 19+19 Crossed Lines Blue Laser, 7 Parallel Lines Blue Laser, Support Marker-Free Laser 3D scanning and VCSEL Infrared Light
EINSTAR Rockit Wireless Laser 3D Scanner, 19+19 Crossed Lines Blue Laser, 7 Parallel Lines Blue Laser, Support Marker-Free Laser 3D scanning and VCSEL Infrared Light
Creality 3D Scanner Sermoon S1 and Scan Bridge Wireless Scanning | 0.02mm High-Precision Blue Laser & Structured Light | Up to 4.6M Measurements/s | Color Texture Mapping | Indoor & Outdoor Use
Creality 3D Scanner Sermoon S1 and Scan Bridge Wireless Scanning | 0.02mm High-Precision Blue Laser & Structured Light | Up to 4.6M Measurements/s | Color Texture Mapping | Indoor & Outdoor Use
Shining 3D EinScan Rigil 3D Scanner All-in-one Wireless 19+19 Crossed Laser Lines, 7 Parallel Laser Lines, VCESL Infrared, Marker Free Blue Laser 3D Scanners, 0.04mm High Volumetric Accruacy
Shining 3D EinScan Rigil 3D Scanner All-in-one Wireless 19+19 Crossed Laser Lines, 7 Parallel Laser Lines, VCESL Infrared, Marker Free Blue Laser 3D Scanners, 0.04mm High Volumetric Accruacy
Revopoint MIRACO Plus 3D Scanner for 3D Printing Handheld, 3D Printer Scanner with Photogrammetry, Up to 0.02mm Precision, Full-Color Scan for Small to Large Objects, 32GB RAM
Revopoint MIRACO Plus 3D Scanner for 3D Printing Handheld, 3D Printer Scanner with Photogrammetry, Up to 0.02mm Precision, Full-Color Scan for Small to Large Objects, 32GB RAM
EinScan H2 Hybrid LED and Infrared Light Source Handheld Color 3D Scanner with Solid Edge Shining3D Version CAD Software
EinScan H2 Hybrid LED and Infrared Light Source Handheld Color 3D Scanner with Solid Edge Shining3D Version CAD Software
Our technology thoroughly searches through the online shopping world, reviewing hundreds of sites. We then process and analyze this information, updating in real-time to bring you the latest top-rated products. This way, you always get the best and most current options available.